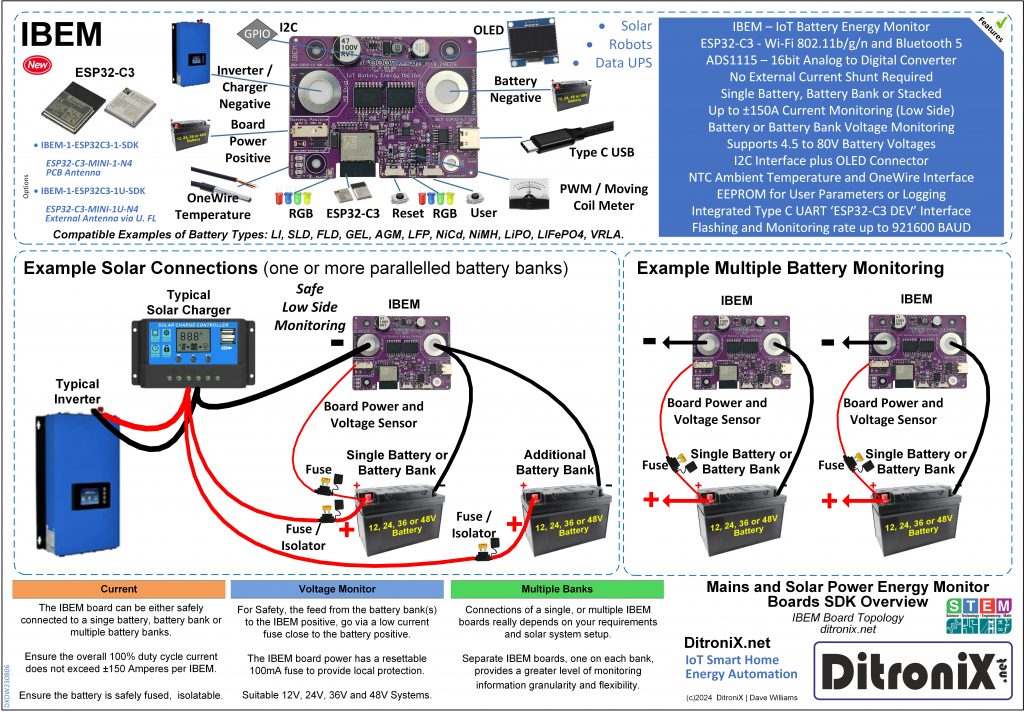
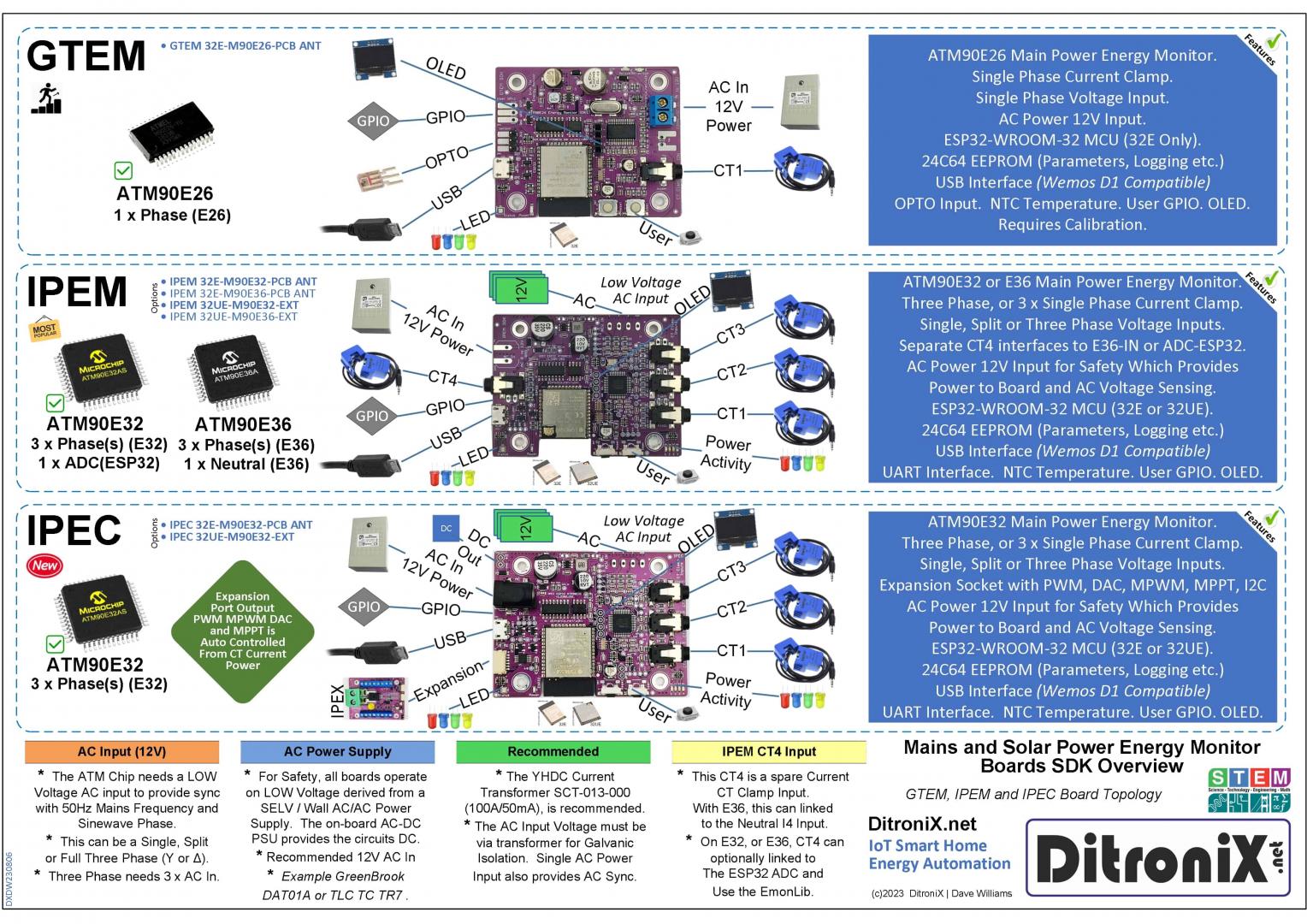
Welcome to DitroniX.net for Internet of Things (IoT), Home Automation, Energy Monitoring, Smart Energy and Electronic Innovation Boards for the Electronics Hobbyist and STEM Maker Community.
Our online shop has moved to eBay and Amazon. More of our products are being added to these sites.

 Please visit our evolving GitHub Repository and associated Wiki Pages within the Repositories, containing Sample Code, OpenSource firmware, Technical and Support Knowledge-base, Datasheets and Information.
Please visit our evolving GitHub Repository and associated Wiki Pages within the Repositories, containing Sample Code, OpenSource firmware, Technical and Support Knowledge-base, Datasheets and Information.
STEM project information is also available on hackster.io/ditronix
Should you have any queries, or have direct R&D or sales requirements, please feel free to Contact Us
All our boards and related products are Designed and Manufactured in Great Britain. This site is a subset of DitroniX.Com
Supporting the engagement, interest and careers of people, of all ages, through the fascinating World of STEM Learning and Amateur Radio & Electronics. DitroniX, planting a seed in Electronics, for our future engineers.
 |  |  |  |  |  |
(C) 1981-2024 DitroniX Ltd | Dave Williams | G8PUO